1. Global Supply Fundamentals: Transitioning from “Surplus Digestion” to “Supply Tightening”
Over the past two years, the global tomato paste market has transitioned from a period of capacity expansion—driven by the extreme price highs of 2022—to a price correction in 2024 caused by surplus inventory. As we enter the 2026-2027 cycle, the market is showing clear signals of a turnaround:
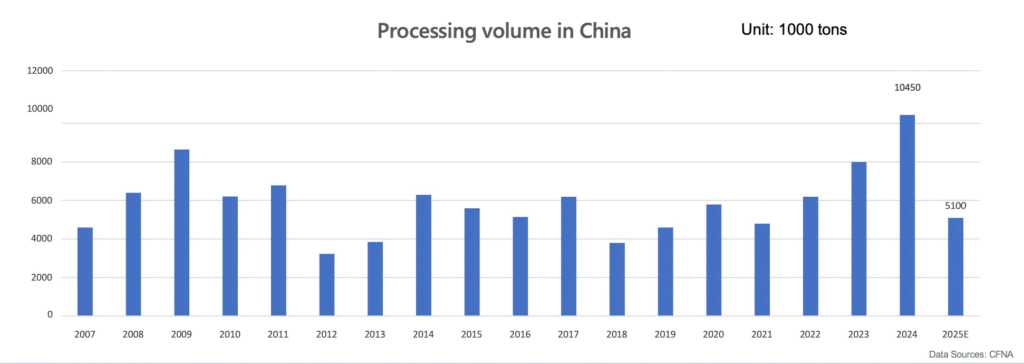
- Inventory Pressure Relief: With the conclusion of the 2024 production season and the strategic production cuts projected for 2025 (China’s processing volume is expected to drop to 5.1 million tons), the market has entered an active de-stocking phase.
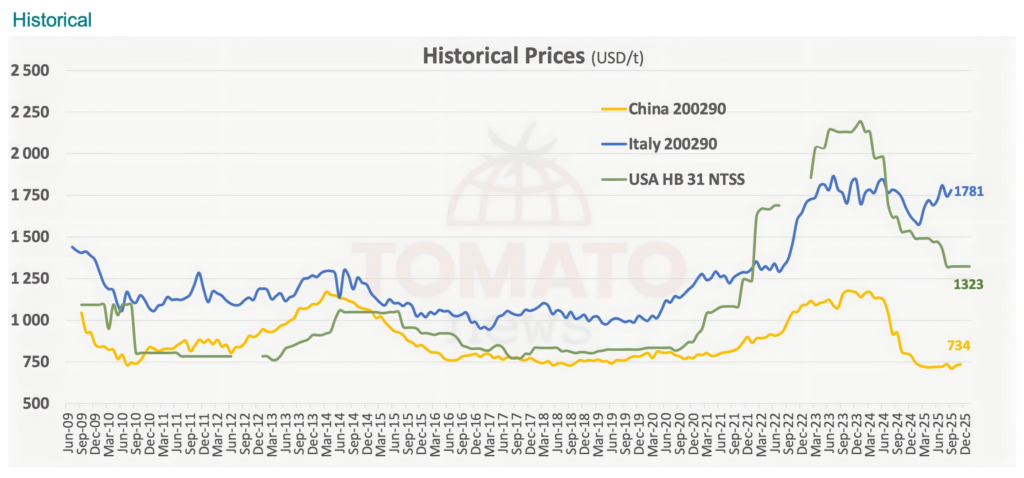
- Price Bottoming and Rebuilding: The unit price of Chinese tomato paste hit a low point in 2024 (approx. $734/ton). However, as inventories are consumed, prices have stabilized and entered an upward trajectory.
- Steady Import Demand: Data from the top 20 importing countries shows that the import volume of bulk tomato paste maintains a steady average annual growth rate of approximately 2%, indicating resilient global industrial demand.
2. Core Variable: The Ripple Effect of the 15% Reduction in U.S. Production
As California is a central bellwether for global tomato paste pricing, its production fluctuations will have a profound impact on the 2026 market:
- Widening Supply-Demand Gap: The projected 15% reduction in U.S. output will significantly decrease the global supply of high-end raw materials, forcing multinational food giants to seek alternative sources globally.
- Creating Market Space for Chinese Exports: Historical trends show that when California reduces production due to climate or policy, international prices typically surge. This will directly weaken the international competitiveness of U.S. paste, providing an excellent window for Chinese exporters to penetrate North American peripheral markets and high-standard industrial sectors.
- Price Upward Pressure: Combined with the U.S. production cut expectations, tomato paste prices for the 2026 season are anticipated to show a substantial increase compared to 2025.
3. China Production Region: Capacity Adjustment and Price Recovery
China, a key global production hub, is proactively adjusting capacity to counter previous low pricing:
- Sharp Decline in Active Factories: Only 82 factories are expected to operate this season, 24 fewer than in 2024, leading to a 22% decrease in daily production capacity. This reduction is conducive to a rapid rebalancing of domestic supply and demand.
- 2026 Season Rebound Expectations: While the number of operating personnel is expected to increase for the 2026 season, it is predicted to remain within a rational range and not return to historical peaks.
- Cost and Logistics Dividends: High-quality paste produced during the 2024 season will enter its final sales window in the first half of 2026. By leveraging the cyclical low freight rates between February and May, Chinese enterprises can capture market share through more competitive Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) pricing.
4. Future Outlook and Strategic Recommendations
- Establishment of an Upward Price Cycle: Driven by the U.S. production cuts and China’s capacity optimization, the price of tomato paste in 2026-2027 is expected to be higher than in 2024-2025.
- Seize the Logistics Window: Exporters are advised to focus on the period after the Spring Festival (Feb–May) when freight rates are lower to accelerate the global distribution of 2024 and 2025 inventories.
